Avoiding Bad Research Practices Through Pre-registration

How do you avoid bad research practices? The answer is by using pre-registration. Find out what it is and how you can use it here.
Investigations must be conducted in an ethical manner. Researchers must meet ethical standards to ensure the validity of their research. In the past, however, some researchers have employed poor research practices.
These practices mainly involve committing minor infringements in order to be able to proceed with the investigation and eventually publish the investigation.
The goal of modern research dynamics is to publish results. However, this goal may put negative pressure on the researchers.
So it is common for many of them to resort to poor research practices. Throughout history there have been very shocking cases. An example is the Stanford prison experiment and the case of Diederik Stapel.
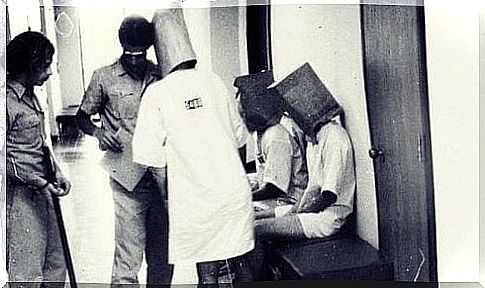
Major fraud
The Stanford Prison Experiment is one of the most famous studies in social psychology. However, some recordings came to light demonstrating the poor research practices used to conduct this experiment.
For example, they relied on anecdotal evidence, trained the guards, and gave implicit orders. They misinterpreted the results. Ever since this was discovered, people have debated whether this research should still appear in textbooks.
Diederik Stapel was a professor of social psychology at Tilburg University. In 2011, it was discovered that Stapel had falsified the data of many of his studies. Instead of using subjects in his studies, he had made up data in such a way that he always got the results he expected.
His students were not aware of these poor research practices. They trusted their teacher. That went on until one of his doctoral students thought it strange that he always got the expected results. From that moment everything collapsed.
Bad research practices
Although these cases have been discovered, they still belong to a minority. After all, most bad research practices are more subtle. These are the most common negative professional practices:
- P-hacking: To test the hypotheses of statistical analyses, researchers use the p-value. It is usually 0.05. However, when they use many variables and experimental conditions, this value can be affected. Therefore, it is recommended to reduce this value. Researchers should do this before conducting the study.
- Low Power: A sample of small size can cause the study to have low static power. In turn, a low power is likely to lead to a false positive. In other words, the research will claim something that does not actually exist.
- Harken: This means that the researchers change the hypothesis as soon as they notice that the results are not what they initially expected.
What is pre-registration and how can it help to avoid bad research practices?
Pre-registration is one solution to avoid these bad research practices. Pre-registration means that the objective of the research and the methods that the researchers will use are made public. Anyone can therefore check whether the researchers conducted the study in an ethical manner or as they previously claimed.
Pre-registration is very easy. There are websites that can help you with this. For example, you have the Open Science Framework (OSF). On this site you can find different templates for pre-registration.
You can also upload any research material (databases, questionnaires, supplementary material, etc.). You can then make the research public in a simple way.

How can you pre-register?
In the Open Science Framework you can find several pre-registration templates. Some templates require more information than others. As an example, let’s take one of the simplest templates, called AsPredicted. You must complete the following sections:
- The data: Have you already collected the data or will you collect it after the pre-registration.
- Research hypothesis: Explain the hypothesis you want to test.
- Variables: What are the variables in the study and how are you going to measure them.
- The circumstances: What circumstances will you assign to the participants (for example, control and experimental).
- The analysis: which analysis will you perform once you have collected the data.
- Observations: The number of observations you will collect. In other words, this concerns the number of participants you need.
By making the data of the studies public, they are visible to everyone. The chance that someone will use bad research practices therefore decreases. Pre-registration requires more time. After all, you have to think about what you will investigate. Yet many people apply it. In addition, it ensures that science is more transparent.